
Non sterile isolation gown
- Packung mit 100 Stück Packung mit 100 Stück

Nous contacter : 01 48 01 32 89
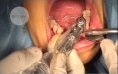
HYGITECH Academy invites you to watch this clinical case on dental implant placement after bone...
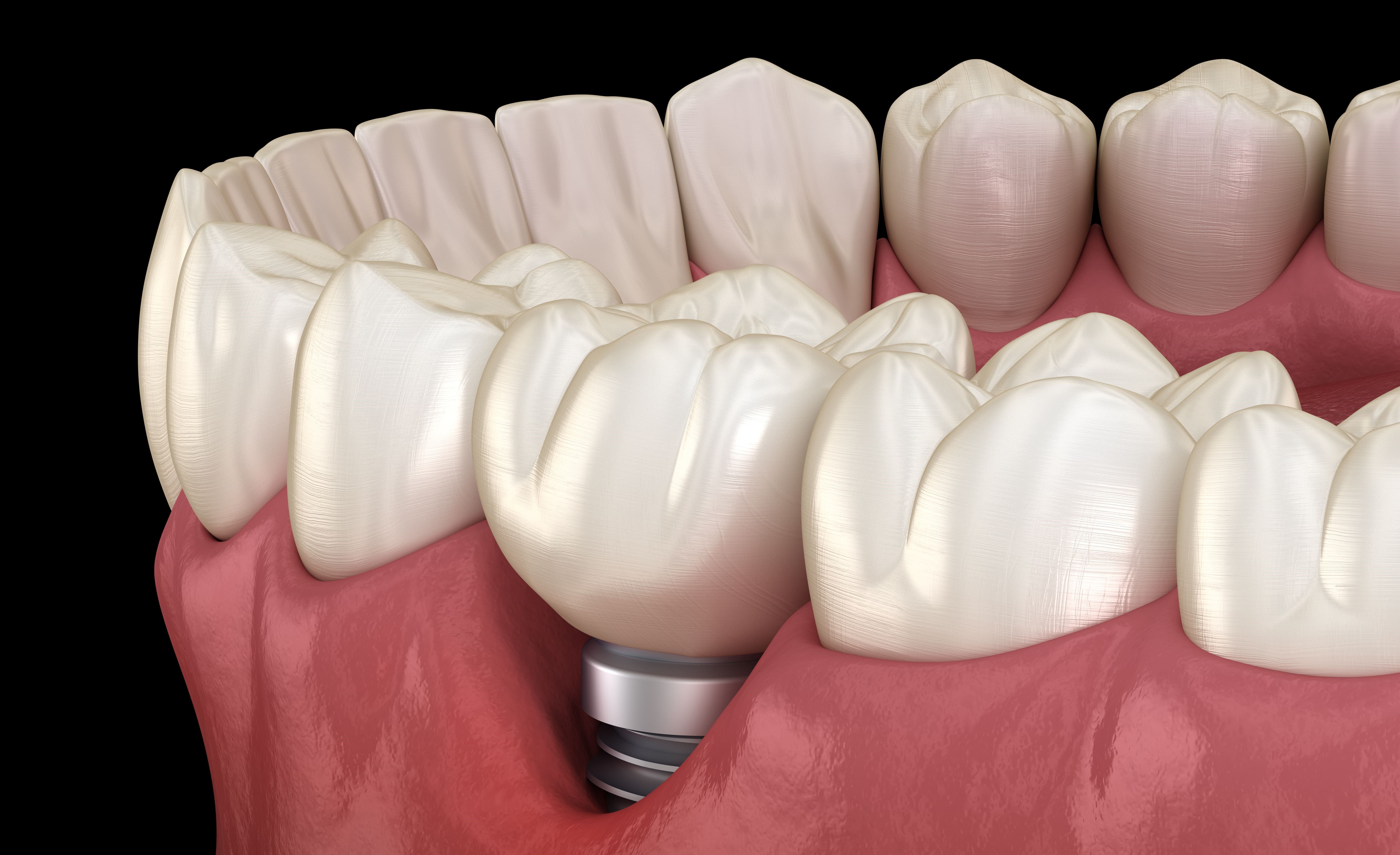
Further to the anatomical-histological review of periodontal and peri-implant tissues, this...

Implant unit motors are necessary equipment for placing dental implants. They are composed of a...
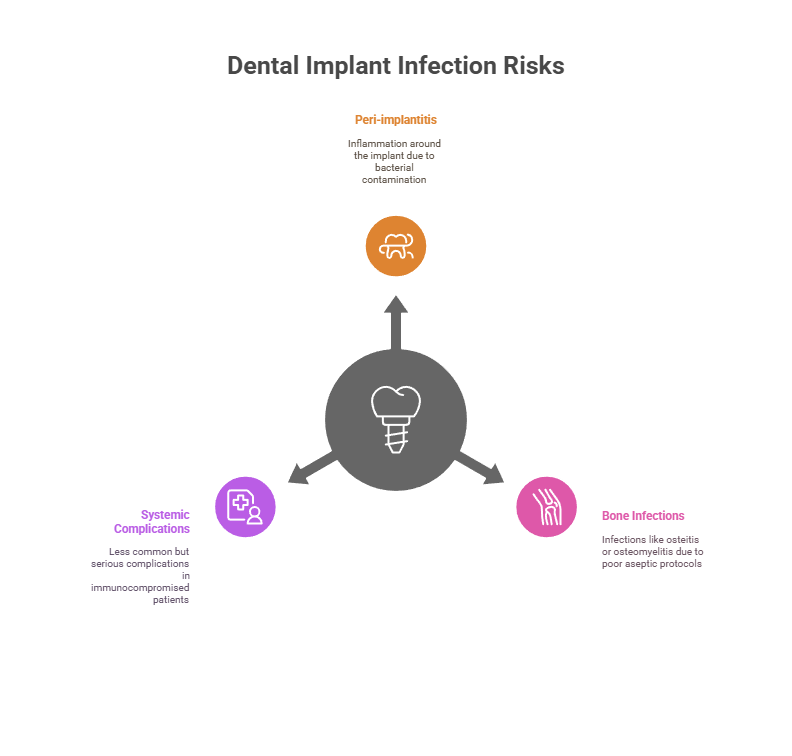
The surgical oral environment is naturally exposed to a high bacterial load, making infection risk prevention essential. Postoperative infections can lead to serious consequences, including:
Peri-implantitis: inflammation of the peri-implant tissues, often caused by bacterial contamination during implant placement or poor postoperative hygiene.
Bone infections: such as osteitis or osteomyelitis, particularly when aseptic protocols are not followed.
Systemic complications (less common), especially in immunocompromised patients or those with comorbidities (diabetes, cardiovascular disease, etc.).
Healthcare professionals are exposed to biological risks, particularly during invasive procedures:
Exposure to blood and body fluids (e.g., needlestick injuries and other blood exposure incidents).
Transmission of infectious agents such as hepatitis B and C viruses, HIV, or tuberculosis.
Contaminated aerosols generated by rotary instruments or ultrasonic devices, which may contain airborne pathogens (e.g., SARS-CoV-2).
Infections may originate from:
The patient’s oral flora.
Contaminated instruments that are improperly sterilized.
A non-sterile surgical field or asepsis breaches (e.g., poor hand hygiene, torn gloves).
Improper surgical site preparation (e.g., no antiseptic rinsing, insufficient contact time with disinfectants).
Use of single-use sterile kits (such as HYGITECH surgical kits).
Preparation of the surgical field: antiseptics, draping, surgical suction.
Surgical hand washing, use of sterile gloves, FFP2 masks, and face shields.
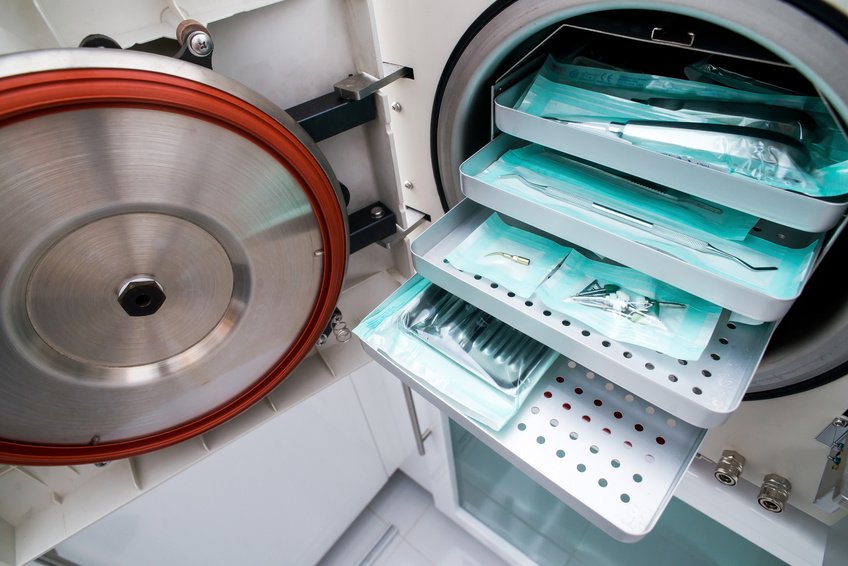
Strict adherence to protocols for disinfection, cleaning, packaging, and sterilization.
Monitoring the effectiveness of sterilization (e.g., Bowie-Dick tests, chemical and biological indicators).
Written, displayed, and enforced protocols.
Regular training on infection risks for the entire team.
According to HAS and ADF guidelines, any invasive procedure must follow strict surgical asepsis principles to prevent infections. The ANSM also emphasizes the importance of traceability for sterile medical devices.
HYGITECH recommendations
To reduce infectious risks, we recommend:
HYGITECH single-use surgical kits
Sterile drapes and gowns
Single-use sterile surgical suction
Sur le sujet

ADAPTATEURS CANULES HYGITECH (1)
