
Protect extend kit
- Best quality / price ratio Best quality / price rat…
- Sterile Sterile
- 48 items in the kit 48 items in the kit

Nous contacter : 01 48 01 32 89
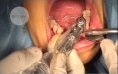
HYGITECH Academy invites you to watch this clinical case on dental implant placement after bone...
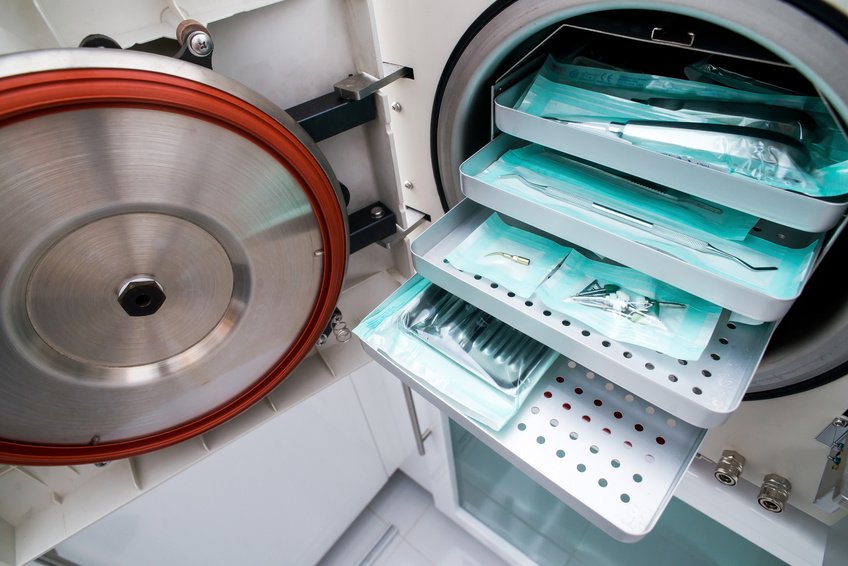
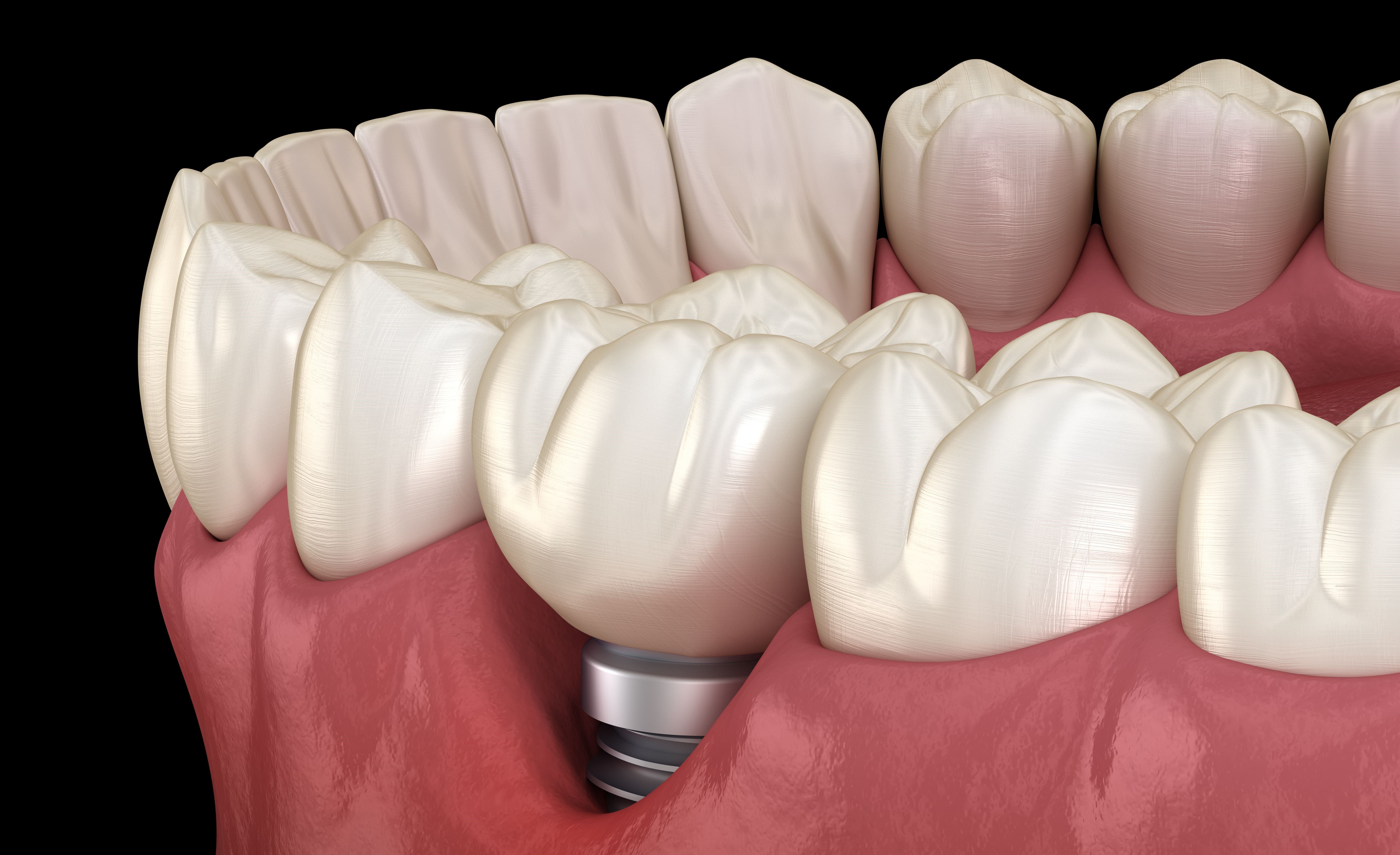

The sterilization of medical devices is an essential step to ensure the safety of care. However, certain instruments, known as thermosensitive, cannot withstand the high temperatures of an autoclave. Their treatment relies on high-level disinfection, often performed by cold immersion in specific chemical solutions. When properly executed, this method provides a reliable alternative to traditional sterilization.
An instrument is considered thermosensitive when it cannot be exposed to temperatures above 60–70°C without risk of damage. This category includes:
Certain plastic or fiber-optic materials (e.g., surgical suction tips, intraoral cameras),
Instruments containing electronic components,
Reusable devices that cannot be disassembled.
These instruments cannot undergo sterilization via saturated steam (autoclave), requiring a strict cold chemical disinfection protocol.
High-level disinfection aims to eliminate the majority of microorganisms, including viruses and multi-resistant bacteria. Although it does not always replace full sterilization, it ensures an acceptable safety level for non-critical or semi-critical devices, according to Spaulding’s classification.
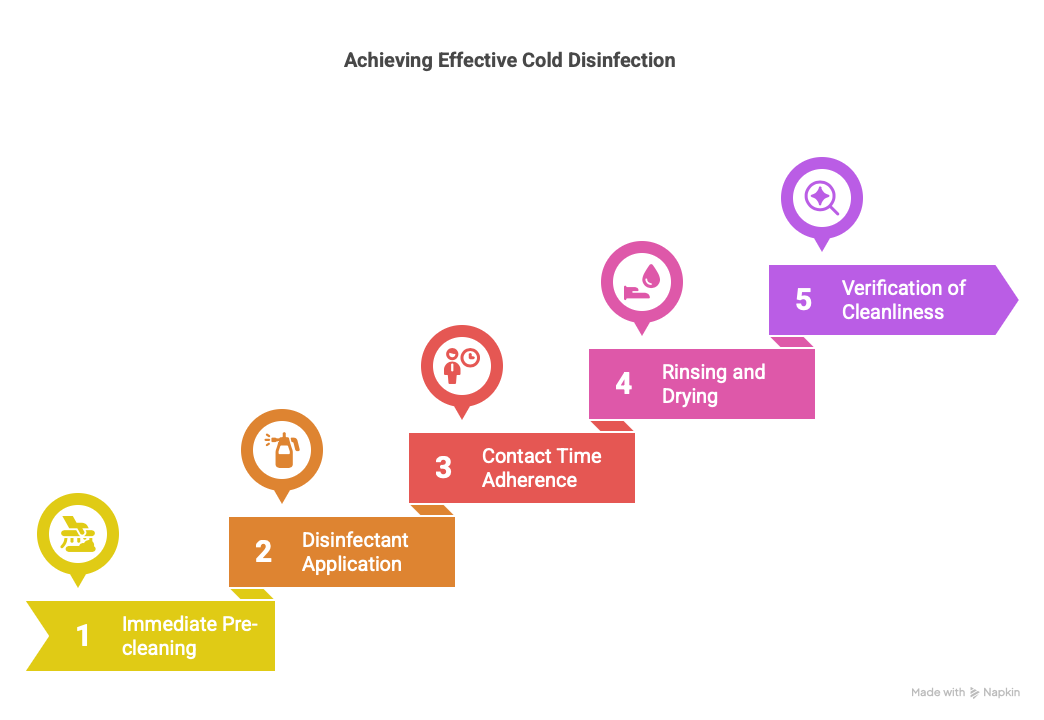
Remove visible contaminants immediately after use.
Use a non-foaming enzymatic detergent compatible with the materials.
Carefully brush instruments submerged in a cleaning solution.
Rinse thoroughly with purified water.
Use a validated high-level disinfectant (e.g., glutaraldehyde, ortho-phthalaldehyde, peracetic acid).
Strictly adhere to the contact time recommended by the manufacturer (usually between 10 and 30 minutes).
Maintain a stable room temperature during immersion.
Rinse with sterile or purified water to eliminate any chemical residue.
Dry with sterile drapes or in a controlled clean air environment.
Store instruments in clean, sealed, and clearly labeled containers.
Use immediately or within a time frame defined by internal protocols.
Cleaning solutions must be renewed regularly according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Wearing PPE (gloves, goggles, mask) is essential due to the potential toxicity of the chemical agents used.
Cold disinfection does not ensure complete sterility and should only be used for instruments that do not penetrate sterile tissues.
According to ANSM (French National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety, 2020), this cleaning method must be part of a rigorous quality assurance program, including cycle traceability, product monitoring, and regular staff training.


 Protocol of use - mild soap
Protocol of use - mild soap
 Protocol of use - alcohol free disinfectant for surfaces
Protocol of use - alcohol free disinfectant for surfaces
 Protocol of use - surfaces with alcohol
Protocol of use - surfaces with alcohol
 Sterilisation - Recording
Sterilisation - Recording
 Protocol of use - sanitizing gel
Protocol of use - sanitizing gel
